What You Should Know About Biodegradable Plastics

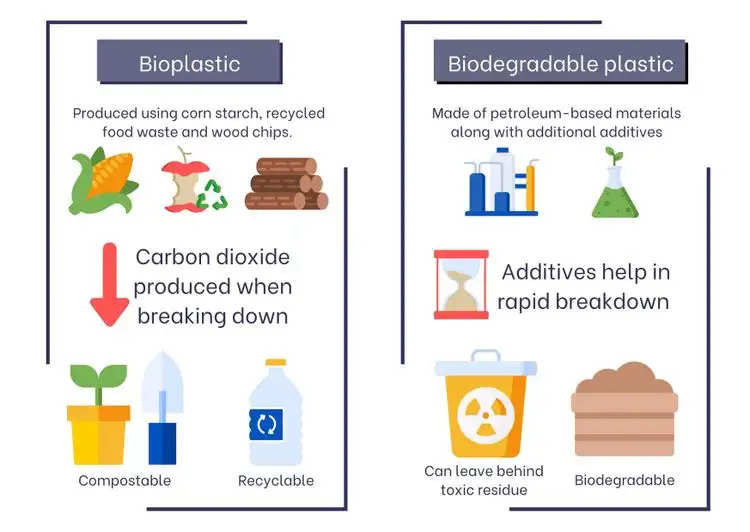
Plastics that can break down spontaneously in the environment are known as biodegradable plastics. Because of their molecular nature, biodegradable plastics decompose quickly in the presence of natural microbes, producing a less hazardous final product.
Because of its undeniable advantages over regular plastics in terms of the environment, biodegradable plastics are thought to be more environmentally benign. This kind of plastic is a better option to reduce environmental pollution, but it is not without drawbacks. Here, we examine the manufacturing process, advantages, drawbacks, and applications of biodegradable polymers.
How Biodegradable plastics are made:
1) A blend of organic bio-based materials, such as cellulose and starch; 2) biodegradable synthetic polyesters derived from fossil fuels; or 3) bio-based oils, like sugarcane, which are not necessarily biodegradable, can be used to make biodegradable plastics.
As a result, they are produced using entirely natural plant or animal ingredients, such as starch, maize oil, orange peels, switchgrass, soybeans, and microorganisms.
Polybutyrate adipate terephthalate (PBAT), polybutylene succinate (PBS), polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH/PVA), and polycaprolactone (PCL) are among the most common examples of such.
Types:
Bioplastics are made fully or in part from polymers derived from biological sources. They can be produced using synthetic polymers or by using plants as a source. Not everything can decompose naturally.
Oxo-degradable plastics are regular plastics that have been treated to speed up their breakdown.
Photo-biodegradable materials require initial oxo-degradation to respond to ultraviolet light.
Hydrolysis starts the breakdown process for polymers that are hydro-biodegradable, which are derived from plant sources like starch.
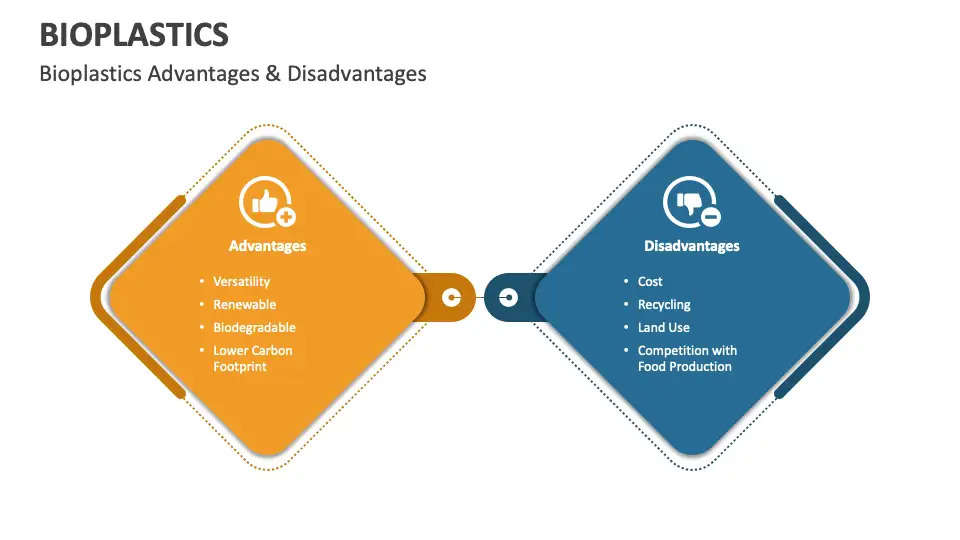
Advantages:
- Recycling Biodegradable Plastics Is Simple.
- Less Energy Is Used in Their Manufacturing.
- When compared to regular plastics, biodegradable plastics use less energy to manufacture.
- Diminishing the Volume of Trash Generated
- Because they decompose more readily, biodegradable polymers are a preferable option.
- Reduced Use of Petroleum
- Compostability
- Lowering of Carbon Dioxide Concentrations
- Lowering of Greenhouse Gas Emission Levels
- When biodegradable plastic products break down, no harmful substances are released.
Disadvantages:
- Engineering Issues
- Expensive Equipment Is Needed for Processing and Recycling
- The danger of Contamination Because It's Hard to Tell Which Plastics Are Biodegradable and Which Aren't
- Methane Production by Biodegradable Plastics in Landfills
- Unexpectedly, problems with ocean pollution cannot be resolved by biodegradable plastics. Because the ocean is too cold for certain forms of plastics to break down, they cannot. Consequently, it poses health risks to marine creatures.
- For the manufacture of biodegradable plastics, additional crops and agricultural land are required.
- The Cost of Biodegradable Products Is Greater
- Water is Needed for Biodegradable Plastics to Effectively Decompose.